News
Industrial
What are the sensors that are hidden behind the smartphone?
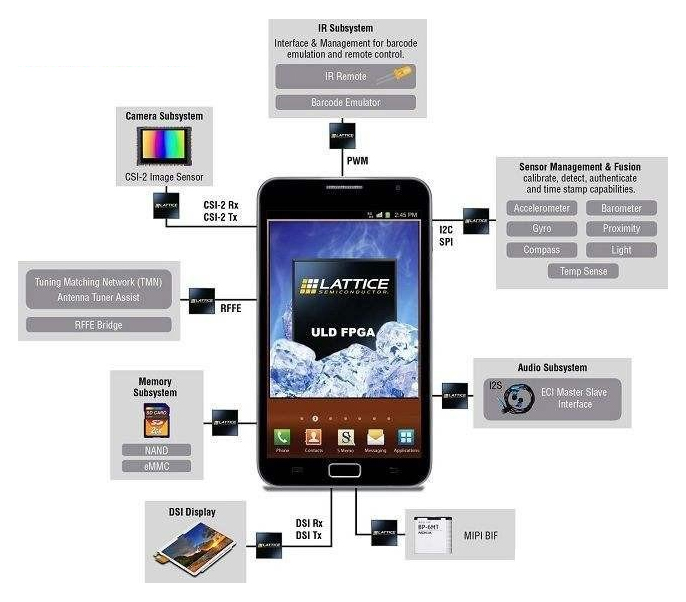
The reason why a smartphone is called intelligence is that it has additional attributes that traditional communication devices do not have. Smartphones are moving further and further on the road of intelligence. We use mobile phones to solve most problems on weekdays, and benefit from Internet, games, navigation, payment, etc. There are a lot of sensors in the phone that work silently in the background to support our front-end operation. You may just see a bunch of sensors when you look at the phone parameters, but do you know what responsibilities these sensors have? The powerful performance and integration of the mobile SoC chip gives the smartphone a greater computing power, but it is the sensors behind the phone that enhance the user interaction experience. Today we will discuss what the various sensors in the phone do.
GPS position sensor
The main function of the GPS module is to receive satellite coordinate information through the antenna to help the user locate. With the popularity of 4G networks, GPS is being used in more scenarios, such as remote positioning monitoring with intelligent hardware, or positioning after device loss. Here we need to distinguish a concept. The mobile phone is generally equipped with A-GPS. The so-called A-GPS is a faster positioning through the mobile network based on receiving the navigation satellite signal, which is more advanced than the ordinary GPS.
distance sensor
The distance sensor is usually placed next to the handset of the handset to detect the distance between the front of the phone and other objects. If the distance reaches a threshold, the screen will be automatically turned off, one will save power, and the other will prevent the touch screen of the mobile phone from being mishandled.
Usually, the distance sensor will be applied to two aspects on the mobile phone. First, when the phone is on the phone, the phone will automatically turn off the screen when it is close to the head, so as to prevent the ear or face from being mishandled on the touch screen, and the screen can be saved when the call is closed. The mobile phone will automatically light off when it is removed from the ear; the second is to prevent the mobile phone from appearing in the pocket or the bag and the screen is lit. If the distance sensor senses that there is an object at a close distance, the mobile phone will be notified to automatically close the screen.
Air pressure sensor
The air pressure sensor has been used in military mobile phones before, and is divided into a variable displacement air pressure sensor and a variable resistance air pressure sensor. A change in air pressure causes a change in the resistance or capacitance measurement. General GPS can calculate your position, but for some height changes you need a barometric pressure sensor to measure. A mobile phone with this sensor can measure how many floors you have on a day, or for indoor positioning, and the internal air pressure sensor is mainly the degree of test equipment closure.
Light sensor
Smartphones usually have such a setting - automatic brightness adjustment, the phone will automatically adjust the brightness of the phone screen according to the intensity of the surrounding light. In the sunny outdoor, the brightness of the screen will automatically increase to help people see the screen under strong light; in the dark night, the screen brightness will automatically become smaller, reducing the light on the eyes, and you can save electricity. The light sensor is used to feel the intensity of the surrounding light to achieve automatic adjustment of the brightness of the screen of the mobile phone.
Light sensors and distance sensors are often integrated into one location, reducing the opening of the front panel and making it look better. The well-known hammer mobile phone integrates the light sensor, distance sensor and mobile phone handset into a long hole from the T1, and the front panel is more uniform.
Temperature Sensor
Many smartphones are equipped with temperature sensors, and some have more than one. The difference is that their purpose is to monitor the inside of the phone and the temperature of the battery. If a component is found to be too hot, the phone will shut down to prevent damage to the phone. In terms of extended functions, the temperature sensor can also detect temperature changes in the outside air, even the user's current body temperature.
Ultraviolet sensor
The ultraviolet sensor uses the photoelectric emission effect to measure, and the outdoor light source is taken by the camera to convert the ultraviolet light intensity into a discharge effect. Mobile phones using such sensors are rare, and the stability of the measurements is subject to further observation. The photoelectric emission effect of certain semiconductors, metals or metal compounds releases a large amount of electrons under ultraviolet irradiation, and the ultraviolet intensity can be calculated by detecting such a discharge effect. The main use is also in the field of sports and health. Detect the level of radiation in the environment. The sensor output current is proportional to the light intensity and the product output has a very high consistency. The sensor has a specific spectral response. The product is mainly used for UV measurement in sunlight and UVA lamp intensity measurement. It is mainly used in mobile phones, smart wearable devices, UV lamp monitoring and so on.
Above we have listed the more mainstream sensors in smartphones, most of which have become standard features of smartphones. We can classify these sensors, for example, some are based on the detection of basic functions, such as light distance sensors, and some are measured on navigation, such as GPS, magnetic field sensors. Others are specifically designed for sports health, such as heart rate blood oxygen sensors, UV sensors, and more. It is these “black technologies” hidden behind the phone that make us more comfortable when using smartphones.
Sensors, like other electronic components, are getting smaller and smaller and cheaper. The future direction of mobile phone sensors will be to think about how to further improve the calculation of intensive reading, and how to integrate more sensors in a limited device to sense the user's current state.

 Collect
Collect
 Navigate:
Navigate: