News
Industrial
Advantages and characteristics of double-row sensors in smart cars
Advantages of a double row sensor
At present, most smart cars use a single-row sensor road detection method. This way, the road information obtained is small, and the state of the smart car and the condition of the road are not well distinguished, causing trouble in control. In order to make up for the shortcomings, a road detection method with a large forward-looking single-row sensor has been formed. This method detects a farther distance and can judge the direction of the road earlier, which compensates for the disadvantage of low detection accuracy to a certain extent, but also It is not possible to effectively distinguish between smart car status and road conditions.
The car model of the game can be used to detect road information by means of camera or sensor. Our car model adopts double-row infrared tracking mode. With large forward-looking double-row sensor, more track information can be obtained, and strategy can be adopted earlier. , forming a better driving track. It is an alternative to using a complex camera solution.
Stable control can be realized in the straight road to accelerate the smoothness; advance in a small curve in the S-curve, reducing the number of travel routes and steering gear adjustments. In the big bend, the effect of early turn and cut inner bend is realized. Especially in the case of turning, the ability to extend the physical recognition distance by the prediction of the curve in front and rear is achieved, thereby making advance actions and reducing the negative effects caused by the proximity of the detection distance, thereby achieving the above effects.
Sensor array layout
In Fig. 1, the sensor position is indicated only by the receiving tube.
Layout description
The front row sensor extends a long distance, and the center of the car deviates from the black line, which will cause a large offset on the front row sensor.
The rear sensor protrudes closer, and the center of the car deviates from the black line, resulting in a small offset on the rear sensor.
The car is controlled by the different sensitivity of the front and rear row sensors to the car offset.
In order to make the front and rear rows show a clearer division of labor and to collect information farther away, we tilt the front row sensor by about 45o, which makes the front row's forward-looking distance larger, which can better reflect the advantages and characteristics of the front row.
Straight track identification method, control strategy
Straight track recognition
(1) Layout of double-row infrared in this way. There are five physical modes for determining the straight path, and the timing of each application is listed behind the table.
Advantages and characteristics of double-row sensors in smart cars
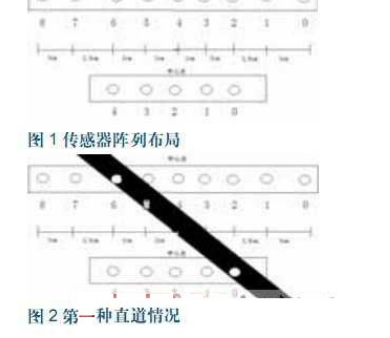
The first straight case (Figure 2)
After the left turn and the big bend, the combination of the front and rear row sensors that are most likely to occur when the bend is detected detects the black line. Suitable for left turn 90° bend, 180° bend. The bending information is obtained in advance, and the steering gear is rotated to a small angle to the left, and an acceleration action is taken at this time to compensate for the lack of foresight. This situation does not satisfy the second recognition method of the straight road when the s curve of the track appears, so it will not accelerate.
The second straight case (Figure 3)
This situation is a reconfirmation of the first case. After turning to the big bend and going through the first situation, after going through this situation, it can be confirmed that the front is straight and the acceleration of the trolley is continued. The control program is switched from the curve program to the straight line stabilization program.
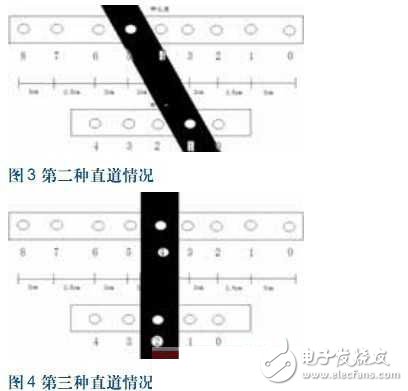
The third straight case (Figure 4)
At this point, linear stability control is adopted. Since the first two cases have been clearly identified as straight, this situation only increases the success rate of straight track recognition.
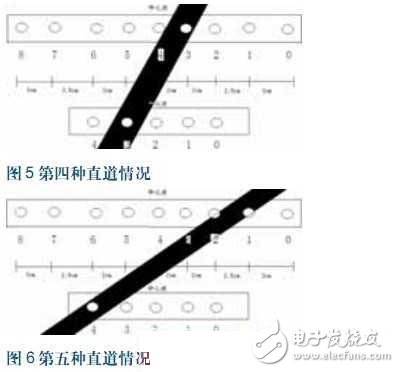
The fourth straight case (Figure 5)
Similar to the second case, the reconfirmation of the fifth case, after turning right and turning to the big bend and going through the fifth situation, and then going through this situation, can confirm that the front is correct and continue to improve the acceleration ability of the car. The control program is switched from the curve program to the straight line stabilization program.
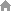
The fifth straight case (Figure 6)
After turning right and turning, the combination of the front and rear row sensors that are most likely to appear when cornering is detected when the black line is detected. Suitable for right turn 90o bend, 180o bend. The bending information is obtained in advance, the steering gear is rotated to a right angle, and an acceleration action is taken at this time to compensate for the lack of foresight. When the s-curve of the track appears, it does not satisfy the second recognition method of the straight road, so it will not accelerate.
(2) Straight track identification, program-assisted confirmation
After entering the corner, as the car travels, it will oscillate, which may not satisfy the above five conditions when exiting the bend. In order to improve the recognition success rate of the straight track, a second straight path discrimination method is added. Both work at the same time. After satisfying the first type, it is straight through the confirmation of up to 15ms.
The program is executed cyclically, and our program execution frequency is 2KHz. Using the timer interrupt (15ms), the three sensors in the middle of the front row (numbered 3, 4, 5) are counted separately using three counters. If one of the execution programs detects a black line, the corresponding counter is incremented by one. . After calculation, the maximum value that can be counted in 15ms is 31. We set the maximum value of the count. If the required count value is reached within 15ms, it is considered to be a straight track. The straight line program is switched and the counter is cleared. If the required count value is not reached within 15ms, the counter is cleared and recounted. . For example, the car is 2m/s and the car is 3cm. We only need to judge the straight road within 2~2.5cm. Therefore, if the maximum count value is 20~25, it is considered to be a straight road and jump out of the curve program.
Of course, a more rigorous method can be used to judge, just adjust the time and count value of the timer interrupt. This condition can always be satisfied after entering the straight track, so as a supplement to the first straight-track discrimination method, the stable and reliable identification of the straight track is ensured.
Straight line stability control strategy
After the car is out of the corner, the smart car will oscillate due to the insensitive response of the steering gear, and then it will stabilize. In order to reduce the oscillation as soon as possible, the following actions are taken to control the movement of the car after the exit:
Set the flag in the curve strategy, enter the line program, identify the flag, and take corrective settings for the formula that controls the steering of the steering gear. The formula is: q=K1q1+K2q2; where q is the control amount finally given to the steering gear, q1 is the return angle value of the front row photoelectric sensor, and q2 is the back row infrared return angle value. K1 and K2 are the weighted ratio values of the front and rear row sensors, respectively. Normally K1 and K2 are 1, and the assignment is changed when needed.
When the car enters the straight road from the curve and successfully recognizes the straight road, the value of K1 is reduced. Since the rear sensor is close to the front wheel (steering wheel) of the trolley, when the center of the trolley deviates from the black line, it will not be lateral in the rear sensor. The position produces a large displacement (relative to the front row of sensors), so the number of times the trolley is adjusted on the straight line will be significantly reduced, and the stability of the straight line will be good. At the same time, according to the combination of different sensors in the front and rear rows, different cornering strategies are given (in the program as a list), and the stability control ability of the straight line is further improved.

 Collect
Collect
 Navigate:
Navigate: